New Study Provides Absolute Dates for Artifacts from Lusatian Urnfield Cemetery at Brzezie, Greater Poland
Archaeologists have made a step toward uncovering the history of the Lusatian Urnfield Cemetery at Brzezie in the Pleszew region of Greater Poland. After many years of fieldwork, including geophysical prospecting and excavation, materials for radiocarbon and luminescence dating were collected to determine the absolute chronology of the site.

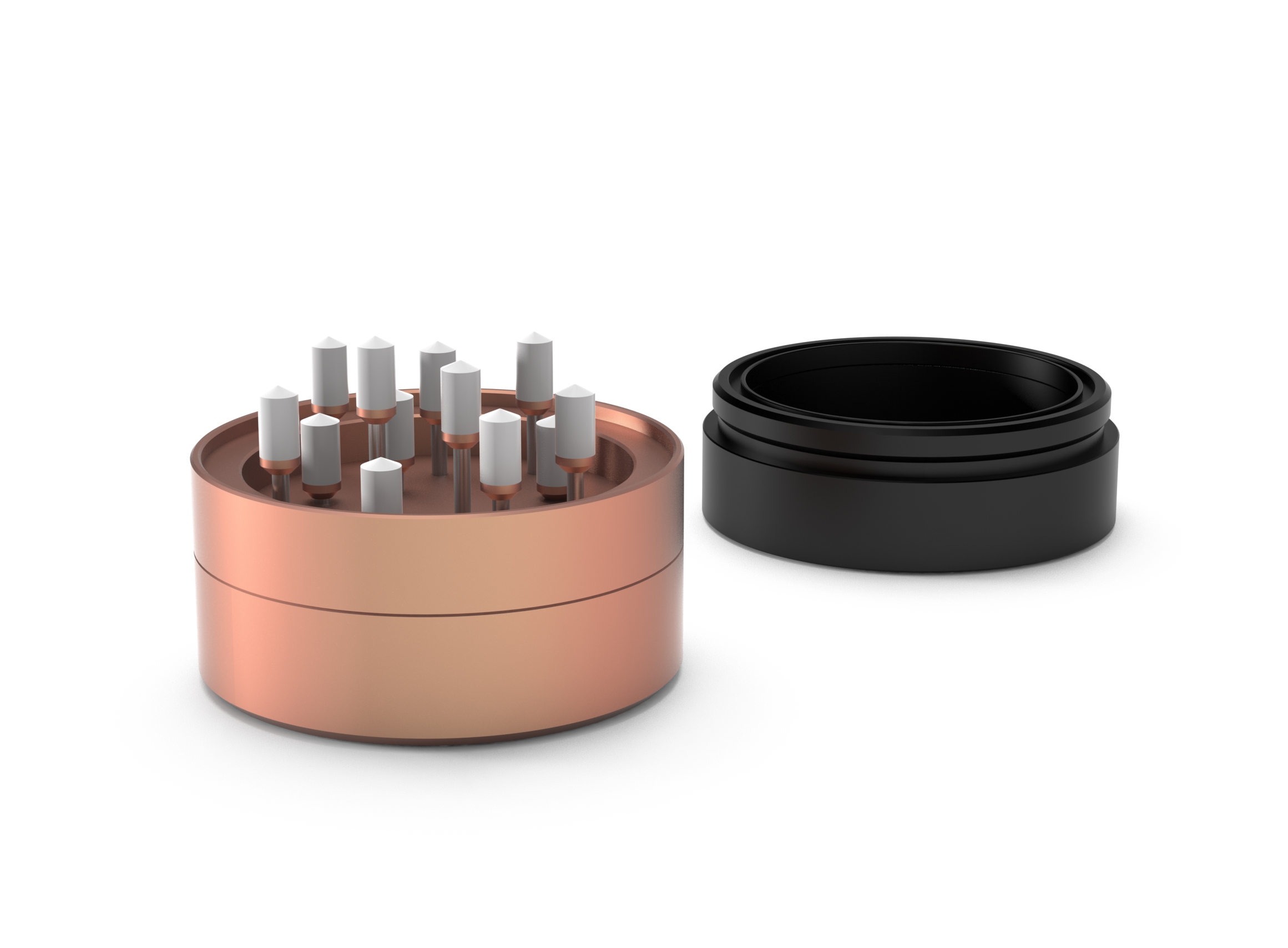
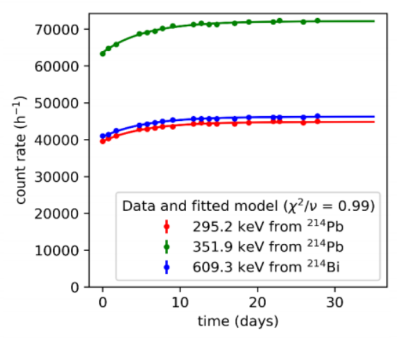
In a study four samples were dated using OSL. The luminescence dating was made possible by measuring the dose rates in small archaeological samples using the innovative uDOSE system. The results reveal an agreement between radiocarbon and OSL dating methods, providing a date range of 1000-500 BC.
This new study provides valuable insights into the history of the Lusatian Urnfield Cemetery at Brzezie and the uDOSE system helped to provide a more accurate estimate of the dose rates for OSL dating.
Ginter, A.; Moska, P.; Poręba, G.; Tudyka, K.; Szymak, A.; Szczurek, G. Absolute Dates of Artifacts from Lusatian Urnfield Cemetery at Brzezie, Greater Poland. Radiocarbon 2022, 64 (6), 1471–1482. https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2022.70